In this post we’ll walk through the process of passing an image (or any file) to a Netlify function using FormData and busboy.
Netlify Functions are serverless functions that allow you to run your backend code without managing any infrastructure. They can be used for various tasks, including processing form submissions, handling file uploads, and integrating with other APIs.
FormData is a web API that enables the easy creation and manipulation of form data to be sent as part of an HTTP request.
busboy is what many Express middleware’s such as multer use under the hood.
Sending an Image File
To send an image file to the function we’ll need a frontend. For demonstration purposes we’ll be using a simple React form with a file input and a submit button. We’ll use axios for making POST requests to the Netlify function. First, install axios as a dependency:
npm install axios
Now, create an UploadForm.tsx component with the following code:
import { useState, ChangeEvent, FormEvent } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
export function UploadForm() {
const [image, setImage] = useState<File | null>(null);
function handleChange(e: ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) {
if (e.target.files) {
setImage(e.target.files[0]);
}
}
async function handleSubmit(e: FormEvent<HTMLFormElement>) {
e.preventDefault();
if (!image) return;
// Create a FormData object and append the image file
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('image', image);
// Send the FormData object to the Netlify function
try {
const { data } = await axios.post(
'/.netlify/functions/upload',
formData,
{
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'multipart/form-data',
},
},
);
console.log('Upload successful:', data);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Upload failed:', error);
}
}
return (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input type='file' accept='image/*' onChange={handleChange} />
<button type='submit'>Uploadbutton>
form>
);
}
The UploadForm component allows users to select an image file and submit the form. When the form is submitted, it creates a FormData object, appends the selected image, and sends a POST request to the Netlify function.
Configuring the Function & Parsing the Payload
First we’ll need to install busboy & @netlify/functions:
npm install busboy
npm install @netlify/functions
npm install --save-dev @types/busboy // If using TypeScript
Now create a new directory named netlify in your project’s root directory, then add a folder within there named functions. Inside the netlify/functions directory, create a new file named upload.ts and add the following contents:
import busboy from 'busboy';
import { Handler } from '@netlify/functions';
type Fields = {
image: {
filename: string;
type: string;
content: Buffer;
}[];
};
function parseMultipartForm(event): Promise<Fields> {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
const fields = { image: [] };
const bb = busboy({ headers: event.headers });
bb.on('file', (name, file, info) => {
const { filename, mimeType } = info;
file.on('data', (data) => {
if (!fields[name]) fields[name] = [];
fields[name].push({
filename,
type: mimeType,
content: data,
});
});
});
bb.on('close', () => {
resolve(fields);
});
bb.end(Buffer.from(event.body, 'base64'));
});
}
export const handler: Handler = async (event) => {
try {
const fields = await parseMultipartForm(event);
if (!fields) {
throw new Error('Unable to parse image');
}
console.log('fields is: ', fields);
console.log('image is: ', fields.image);
const image = fields.image[0];
// Handle image however you want here...
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify(image),
};
} catch (error) {
return {
statusCode: 400,
body: error.toString(),
};
}
};
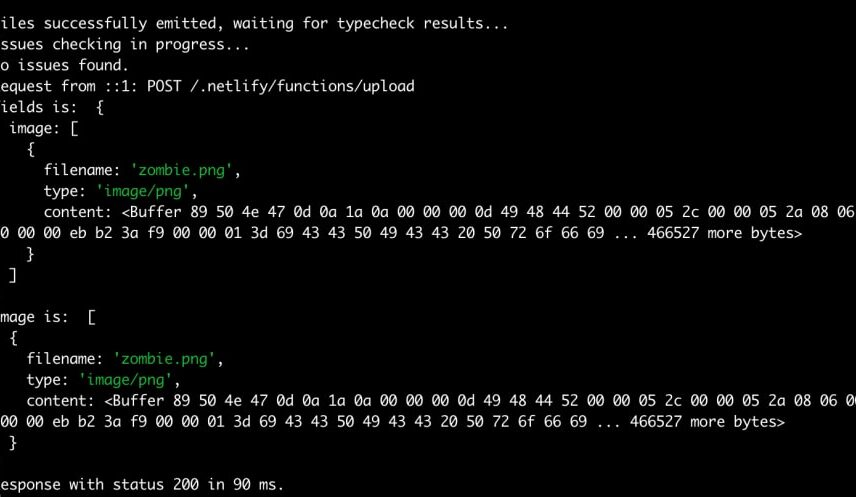
To test your changes, run npx netlify dev which will open a local development window. You can then add an image of your choice via the input and hit submit, which should give you something like this in your terminal:
That’s it! ✅ You now have an image passed and parsed available to do anything you wish with. You can easily extend this approach to handle other types of file uploads or additional form fields. If you wish to deploy your application simply login to Netlify and connect your Git repository within Netlify and hit “Deploy”.